Using a directional remote controller with UWB and IMU technologies

UWB Technology Overview
Ultra-Wideband (UWB) technology is an advanced wireless communication technology that uses ultra-wideband pulse signals for data transmission. UWB offers significant advantages over traditional wireless communication technologies, including wide bandwidth, strong anti-interference capabilities, and low power consumption. As UWB technology enables highly accurate short-range positioning and ranging, it is widely used in fields like the Internet of Things (IoT), smart transportation, and industrial automation. In our directional remote controller design, we leveraged UWB Angle of Arrival (AoA) technology to precisely determine the controller's position and orientation.
About the Solution
Avnet’s Beijing Laboratory uses the TDK IMU and Murata UWB module, which incorporates the NXP SR150 UWB chip. The system layout is shown in the figure below:
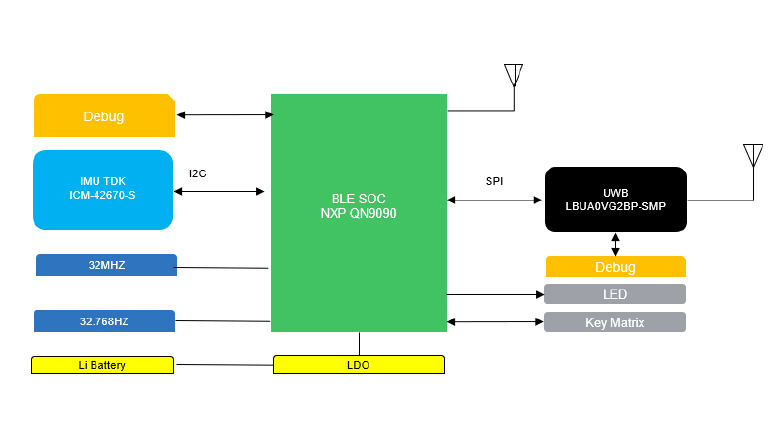
In this solution, the AOA information from the UWB module is used to implement the directional functionality of the mouse. The IMU tracks the mouse’s orientation for precise cursor control, while Bluetooth enables the creation of an HID device, using the absolute descriptor of the HID mouse to control the cursor.
About the NXP SR150 chip
The NXP SR150 is a high-performance UWB chip from NXP that is designed for devices requiring high-precision positioning and low power consumption. At its base is the advanced ARM Cortex-M33 processor architecture, with its robust processing capabilities and energy efficiency, making it suitable for use in battery-powered devices. It supports UWB channels 5 and 9 over a frequency range of 6250 MHz to 8250 MHz, meeting the needs of various application scenarios.
In the directional remote controller, the UWB capabilities of the NXP SR150 chip are leveraged to achieve precise positioning of the controller. It can measure the distance between the controller and the receiver with millimeter-level accuracy and determine the direction the controller is pointing through angle measurements. Its high-precision positioning gives users a mouse-like user experience on the screen, supporting actions such as gliding, dragging, and tapping. In addition, the NXP SR150 chip’s low-power design allows the remote controller to operate for extended periods without repeated charging, providing a better user experience.
Overview of the Murata LBUA0VG2BP-SMP chip
The Murata LBUA0VG2BP-SMP is an ultra-compact UWB module based on the NXP SR150 chip. It integrates the NXP SR150 UWB chip, clock, filters, and peripheral components, and features a resin-molded structure with conformal shielding, all in an extremely small size (6.6 × 5.8 × 1.2 mm), making it ideal for devices with space constraints. The module supports a 3-antenna configuration and allows 2D and 3D AoA measurements, providing robust hardware support for directional remote controllers.
Key features of the Murata LBUA0VG2BP-SMP chip:
- High-precision positioning: Uses UWB technology to achieve millimeter-level accuracy in determining the remote controller’s position and orientation.
- Low-power design: Suitable for battery-powered devices; extends the operational life of the remote controller.
- Compact size: Its small form factor facilitates integration into compact devices, such as remote controllers and smart tags.
- Multi-antenna support: Supports a 3-antenna configuration for 2D and 3D angle measurements, enabling comprehensive directional capabilities for the remote controller.
Overview of the TDK ICM-42670-S chip
The TDK ICM-42670-S is a high-performance Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) chip that integrates a three-axis accelerometer and a three-axis gyroscope. It measures an object's acceleration and angular velocity in real time, providing critical motion data for positioning and navigation systems. The chip utilizes advanced MEMS technology to offer high precision, low noise, and low power consumption, making it widely used in applications such as smartphones, drones, and smart wearables.
Key features of the TDK ICM-42670-S chip:
- High-precision measurement: Accurately measures acceleration and angular velocity, providing reliable motion data for positioning systems.
- Low-noise design: Employs advanced filtering technology to minimize measurement noise, boosting data accuracy.
- Low power consumption: Suitable for battery-powered devices; extends the operational life of the device.
- High level of integration: Combines an accelerometer and gyroscope, reducing the need for external components and simplifying system design.
In the directional remote controller, the TDK ICM-42670-S chip works in tandem with the UWB module to enhance accuracy in positioning and direction. By measuring the controller’s acceleration and angular velocity, the IMU chip compensates for posture changes during movement, improving the precision and stability of UWB positioning. For example, when the user quickly moves the remote controller, the IMU chip can detect the motion status in real time and feed the data back to the UWB module, making the remote controller's direction more accurate. Additionally, the low-power characteristics of the TDK ICM-42670-S chip enable extended use of the remote controller without increasing power consumption.
Contact the author
This is a paid solution. Customers can obtain all the source code developed after paying the fee. If you are interested in learning more about this solution, please fill out the form below:
Demonstration of results
The demonstration video of this solution is below: